Choosing the Right Solar Panels for Agriculture
Incorporating solar panels into agricultural operations can significantly improve energy efficiency and sustainability. With various types of solar panels available, understanding which one suits your agricultural needs is crucial. Below are the common types of solar panels, their benefits, and how to calculate your return on investment (ROI) for solar energy systems.
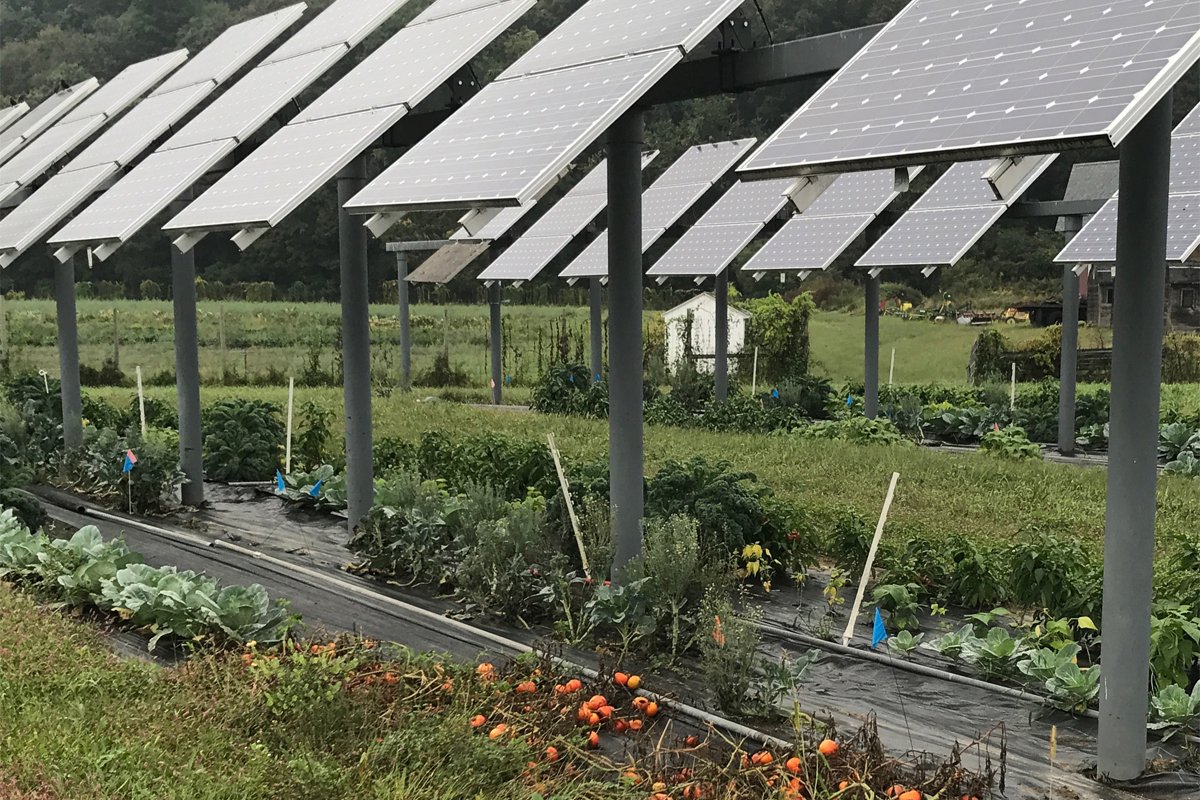

1. Types of Solar Panels
Monocrystalline Solar Panels
Monocrystalline solar panels are recognized for their high efficiency and sleek appearance. Although they tend to be more expensive, their superior performance makes them ideal for agricultural settings with limited space. Their higher efficiency allows for better sunlight conversion, which is essential for powering agricultural equipment and maintaining greenhouse conditions.

Polycrystalline Solar Panels
These panels are more affordable and still provide good efficiency. They are cost-effective for larger agricultural areas where space constraints are less of a factor. Although slightly less efficient than monocrystalline panels, polycrystalline panels can still generate ample power for most agricultural needs.

Thin-Film Solar Panels
Thin-film solar panels are lightweight and flexible, allowing for easier installation in varied agricultural environments, including curved surfaces. While they have lower efficiency compared to crystalline panels, they are durable and can withstand extreme weather conditions, making them suitable for outdoor use.

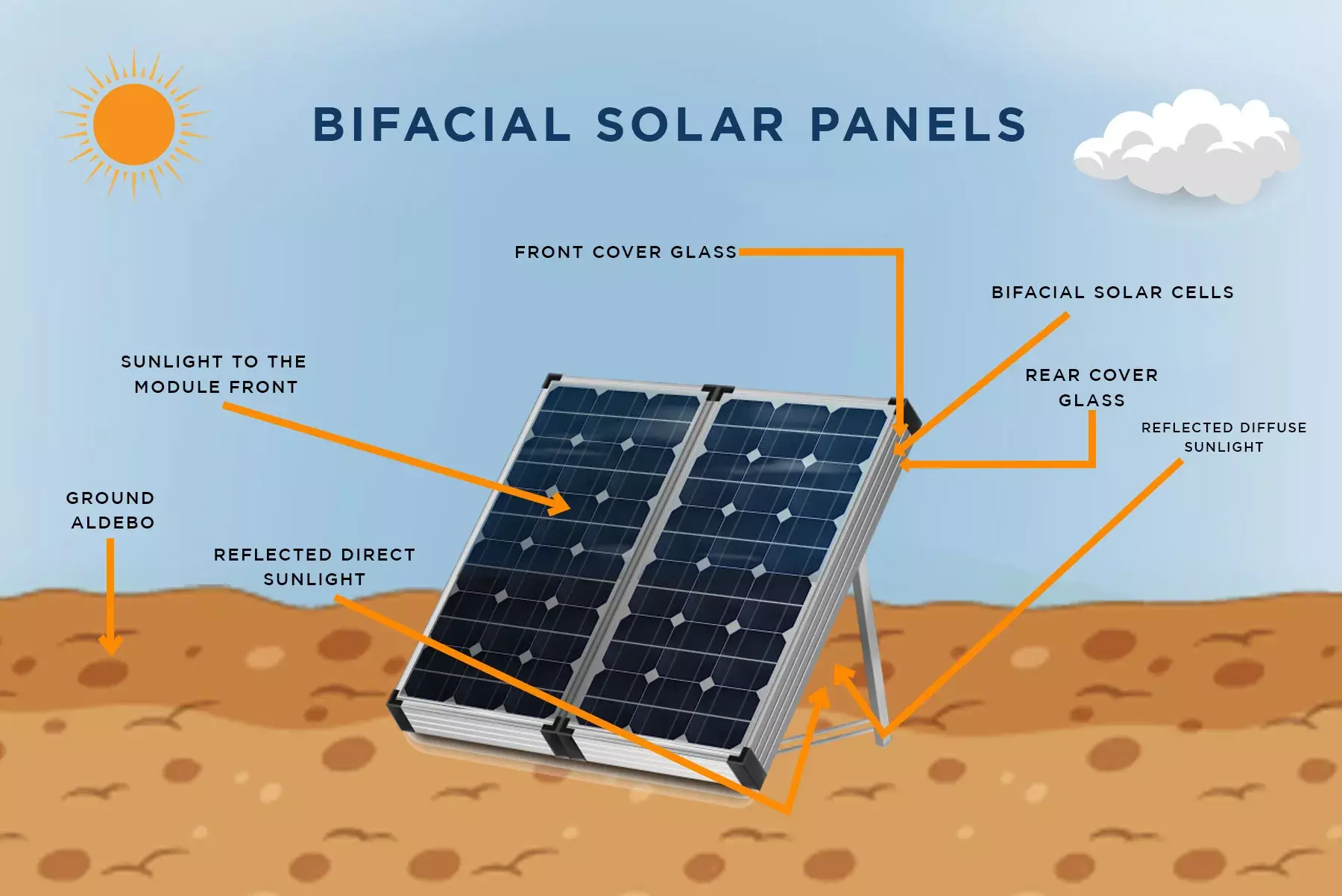
Bifacial Solar Panels
Bifacial solar panels capture sunlight from both sides, enhancing energy generation capabilities. This feature is particularly advantageous in agricultural areas where ground reflection can provide additional light to the panels. Although more expensive, they can maximize energy production, especially when paired with reflective surfaces.
2. Considerations for Choosing Solar Panels in Agriculture
- Energy Demand: Assess the specific energy requirements for irrigation systems, lighting, and heating in greenhouses.
- Budget: Establish a budget that includes installation and potential future costs to narrow down affordable options.
- Panel Type: Research the pros and cons of each panel type to find the best fit for your setup.
- Product Reviews: Read consumer feedback to understand real-world experiences and identify reliable products.
- Manufacturer Reputation: Choose panels from reputable manufacturers known for quality products and good warranty terms.
- Efficiency and Output: Check efficiency ratings and output per square meter to ensure optimal energy conversion.
- Warranty and Lifespan: Look for offers of extended warranties, as durability is crucial for long-term investment.
- Certifications: Ensure panels have proper certifications to guarantee quality standards.
- Compatibility: Verify compatibility with your existing electrical system for seamless integration.
- Customer Support: Evaluate the level of support available from the manufacturer for installation and maintenance.
- Incentives and Discounts: Explore local incentives that can reduce installation costs.
- Environmental Impact: Consider how panels can decrease reliance on fossil fuels and promote sustainable practices.
3. Calculating Return on Investment (ROI) for Solar Panels in Agriculture
Steps to Calculate ROI
- Initial Cost: Calculate the total initial cost, including panels, installation, and additional components.Initial Cost = Cost of Solar Panels + Installation Cost + Additional Components
- Annual Energy Production: Estimate the annual output based on efficiency and sunlight received.Annual Energy Production (kWh) = Panel Efficiency × Area of Panels × Hours of Sunlight per Day × 365 Days
- Electricity Savings: Determine the annual savings on electricity bills.Electricity Savings (currency) = Annual Energy Production (kWh) × Cost of Electricity (currency/kWh)
- Additional Agricultural Benefits: Factor in improved yields or reduced labor costs.Additional Agricultural Benefits (currency) = Improved Crop Yields (currency) + Reduced Labor Costs (currency)
- Total Annual Benefits: Add electricity savings and additional benefits.Total Annual Benefits (currency) = Electricity Savings (currency) + Additional Agricultural Benefits (currency)
- Net Present Value (NPV): Calculate NPV over the system’s lifespan, considering the time value of money.NPV = ∑ (Total Annual Benefits / (1 + Discount Rate)^t) – Initial Cost
- Return on Investment (ROI): Calculate the ROI percentage.ROI (%) = (Total Annual Benefits / Initial Cost) × 100
Conclusion
By carefully selecting the appropriate type of solar panels and calculating the expected ROI, agricultural operations can enhance their sustainability and economic viability. This approach not only provides financial benefits but also contributes positively to the environment, making it a wise investment for modern agriculture.