LFP vs Lead Acid Batteries: A Comprehensive Comparison
LFP vs Lead Acid Cost and Availability
Lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries are generally more cost-effective and widely available compared to lead acid batteries.
The raw materials for LFP batteries, such as lithium, iron, and phosphate, are abundant and less expensive than the materials used in lead acid batteries, which include lead and sulfuric acid.
Lead acid batteries have been around for a longer time and have established supply chains, but the cost of lead can fluctuate due to environmental regulations and mining issues.
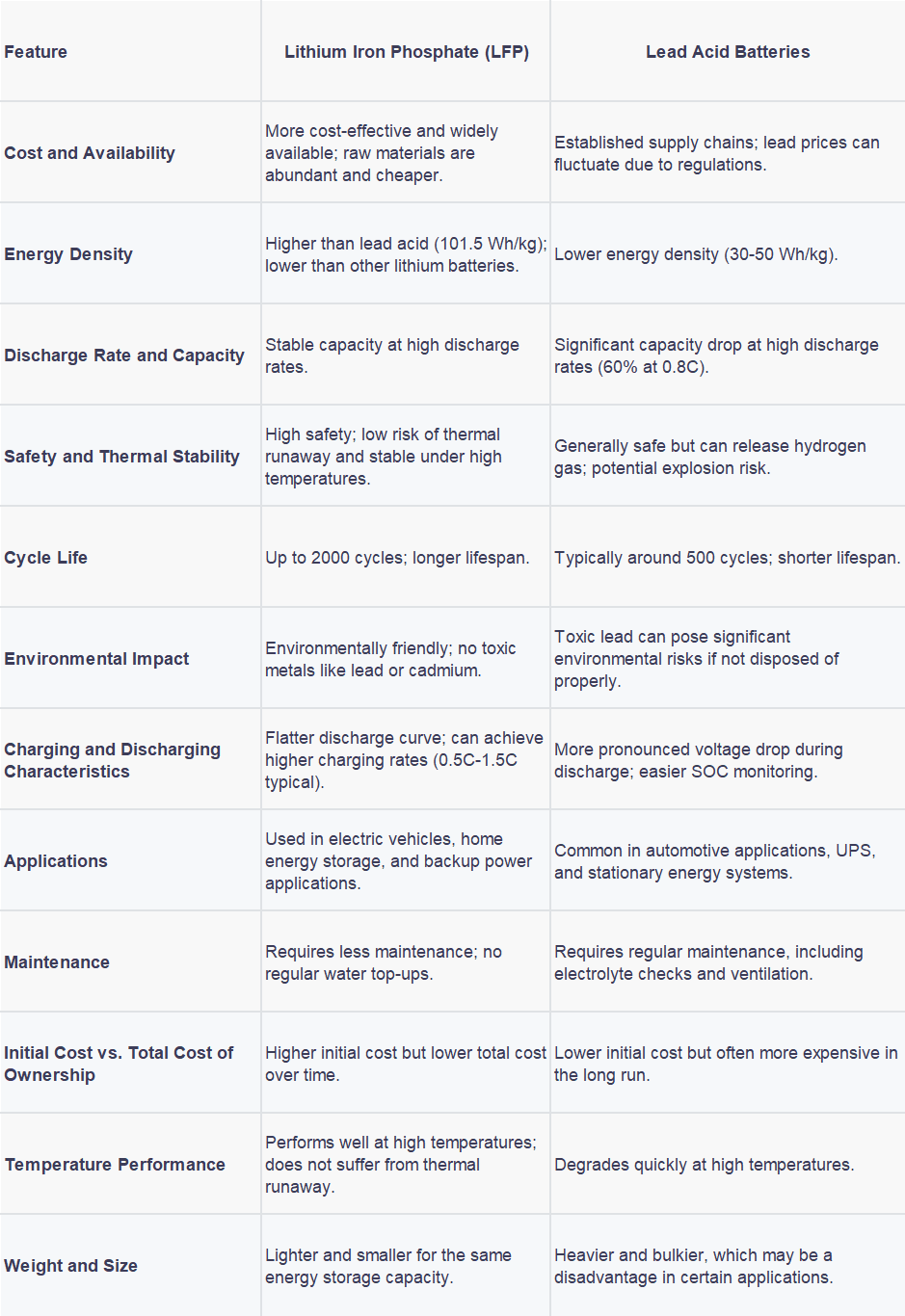
Energy Density
LFP batteries have a lower energy density compared to other lithium-based batteries, such as lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) and nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC) batteries. However, they have a higher energy density than lead acid batteries.
For example, the specific energy of LFP batteries is about 101.5 Wh/kg, while lead acid batteries typically have a specific energy of around 30-50 Wh/kg.
The lower energy density of LFP batteries means they are heavier and bulkier for the same amount of energy storage, but this is often more tolerable in static applications like home energy storage.
LFP vs Lead Acid Discharge Rate and Capacity
LFP batteries show only a small dependence on the discharge rate, meaning their capacity remains relatively stable even at high discharge rates.
Lead acid batteries, on the other hand, experience a significant drop in capacity at high discharge rates. For instance, at a discharge rate of 0.8C, the capacity of a lead acid battery is only 60% of its rated capacity.
This makes LFP batteries more suitable for applications where high discharge rates are common, as a lower-rated LFP battery can often provide a higher actual capacity than a similarly rated lead acid battery.
LFP vs Lead Acid: Safety and Thermal Stability
LFP batteries are known for their high safety and low risk of thermal runaway. They do not decompose at high temperatures and are highly resilient during oxygen loss, which can lead to exothermic reactions in other lithium batteries.
Lead acid batteries are generally considered safe but can release hydrogen gas during charging, which poses a risk of explosion if not properly ventilated.
The carbon coating on LFP cathodes enhances their conductivity, making them suitable for industrial applications and improving their overall safety.
LFP vs Lead Acid Cycle Life
LFP batteries have a much longer cycle life compared to lead acid batteries. LFP batteries can last up to 2000 cycles, while lead acid batteries typically last around 500 cycles.
This longer cycle life reduces the frequency of battery replacements, making LFP batteries more cost-effective over their lifetime.
Environmental Impact
LFP batteries are environmentally friendly because they do not contain toxic metals like lead or cadmium. They also have a lower environmental impact during production and disposal.
Lead acid batteries contain lead, which is toxic and can pose significant environmental risks if not disposed of properly. The production of lead acid batteries also involves more harmful processes.
Charging and Discharging Characteristics
LFP batteries have a flatter discharge curve, which means their voltage remains relatively constant throughout the discharge process. This can make it challenging to accurately monitor the state of charge (SOC), but it also provides a more stable output.
Lead acid batteries have a more pronounced voltage drop during discharge, which can make it easier to monitor SOC but less stable in terms of output voltage.
LFP batteries can achieve higher charging rates, with some research showing potential for 4C-5C super fast charging, though this technology is not yet widely available. Current LFP batteries typically have a best charging rate between 0.5C and 1.5C.
Applications
LFP batteries are increasingly used in electric vehicles, home energy storage systems, and backup power applications due to their cost, safety, and long cycle life.
Lead acid batteries are still commonly used in traditional automotive applications, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and some stationary energy storage systems, especially where weight and size are less critical.
Maintenance
LFP batteries require less maintenance compared to lead acid batteries. They do not need regular water top-ups and can operate over a wider temperature range without significant degradation.
Lead acid batteries require regular maintenance, including checking and topping up electrolyte levels, and ensuring proper ventilation to prevent hydrogen buildup.
Initial Cost vs. Total Cost of Ownership
While the initial cost of LFP batteries may be higher, the total cost of ownership is often lower due to their longer lifespan, lower maintenance requirements, and higher efficiency.
Lead acid batteries are initially cheaper, but their shorter lifespan and higher maintenance costs can make them more expensive in the long run.
LFP vs Lead Acid Temperature Performance
LFP batteries perform well at high temperatures and do not suffer from thermal runaway, making them safer in extreme conditions.
Lead acid batteries can degrade quickly at high temperatures, leading to reduced performance and lifespan.
Weight and Size
LFP batteries are lighter and smaller for the same energy storage capacity compared to lead acid batteries, which is beneficial in mobile applications like electric vehicles.
Lead acid batteries are heavier and bulkier, which can be a disadvantage in applications where weight and size are critical.
Conclusion
In summary, while lead acid batteries have been the standard for many years, LFP batteries offer significant advantages in terms of safety, cycle life, and environmental impact. They are more suitable for modern applications that require high performance and reliability, despite their slightly higher initial cost.